Art therapy emerges as a powerful healing modality for trauma survivors seeking recovery pathways beyond traditional talk therapy. This Trauma therapeutic approach utilizes visual arts, movement, music, and other creative expressions to process traumatic experiences, regulate emotions, and rebuild a sense of safety. The growing popularity of art therapy stems from its ability to access emotions and memories that may be difficult to articulate verbally – making it particularly effective for those who have experienced trauma. Whether you’ve survived military combat, abuse, natural disasters, accidents, or healing childhood trauma, art therapy offers a pathway to recovery.
Understanding Trauma & The Need for Creative Healing
Trauma, as explained by the National Center for PTSD, occurs when overwhelming experiences exceed our capacity to cope, leaving lasting imprints on our nervous system, emotional responses, and behavior patterns. Clinicians categorize trauma as:
- Acute trauma resulting from a single, intense event
- Chronic trauma developing from prolonged exposure to stressful situations, such as that addressed in trauma therapy for domestic violence survivors.
- Complex trauma stemming from repeated interpersonal violations, especially during development
Trauma fundamentally affects brain function. The amygdala (the brain’s alarm system) becomes hyperactive while the prefrontal cortex (our rational thinking center) shows decreased activity. This neurobiological impact explains why many trauma survivors experience persistent hypervigilance, emotional dysregulation, and intrusive memories.
Traditional talk therapy, while valuable, sometimes hits limitations with trauma treatment. The reason lies in how traumatic memories are stored—often as fragmented sensory impressions rather than coherent narratives. These memories may lack verbal components entirely, existing instead as bodily sensations, images, or emotional states. Creative therapy approaches provide alternative pathways to access and process these non-verbal aspects of trauma, allowing healing to occur through multiple channels.
What is Art Therapy for Trauma Survivors?
Art therapy for trauma survivors integrates psychotherapy with creative processes, forming part of comprehensive trauma recovery methods to facilitate healing and recovery. Unlike casual art-making (which still offers benefits), professional art therapy involves structured interventions guided by trained therapists who understand both psychological principles and creative processes.
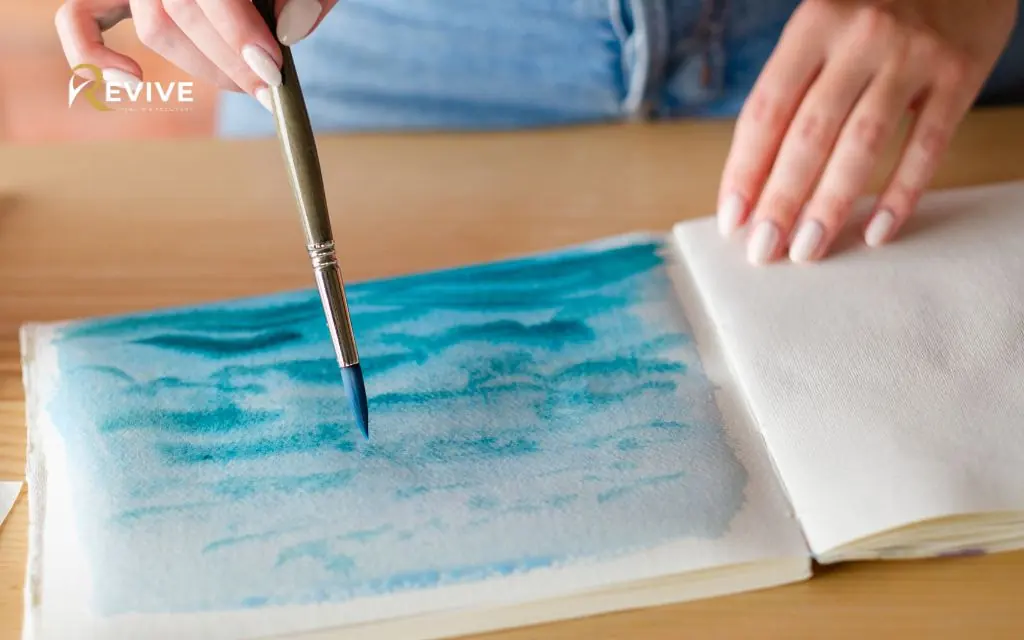

Where cognitive behavioral therapy primarily addresses thought patterns through verbal exchange, art therapy engages multiple sensory systems simultaneously. This multi-sensory approach proves particularly effective for trauma treatment since traumatic memories themselves involve sensory components that often defy verbal description.
Research from neuroscience, such as this study, supports art therapy’s effectiveness. Creating art activates brain regions associated with sensory processing, emotion regulation, and memory integration—precisely the systems disrupted by trauma. The act of making art also releases dopamine, providing natural reinforcement for the therapeutic process. Many trauma survivors discover that creative expression helps integrate fragmented traumatic memories into cohesive narratives, reducing their emotional intensity.
The Foundations of Art Therapy for Trauma
Trauma-informed art therapy rests on fundamental principles that create safety and promote recovery. These include:
- Establishing physical and emotional safety
- Providing choice and control over artistic expression
- Building trust through consistent therapeutic boundaries
- Recognizing the unique nature of each person’s trauma response
The American Art Therapy Association has evolved standards for trauma-focused art therapy practice since its formal establishment in 1969. What began as an experimental approach has developed into a clinically recognized treatment modality supported by research and implemented in various clinical settings.
Safety creation stands as a central achievement of art therapy for trauma survivors. The art-making process itself provides a container for difficult emotions while offering distance through symbolic representation. Many clients report feeling safer exploring traumatic material through art than through direct verbal disclosure.
How Art Therapy Facilitates Trauma Recovery
When trauma renders words inadequate, art provides an alternative communication channel. Trauma survivors often struggle to verbalize their experiences due to overwhelming emotions or fragmented memories. Visual expression circumvents these verbal barriers, allowing internal states to emerge through color, form, and composition.
Art therapy enables the processing of traumatic memories through symbolic representation rather than direct verbal recounting. Creating external representations of internal experiences – whether through drawing, painting, or sculpting – helps survivors gain perspective on their trauma and reduce its overwhelming nature.
Creative engagement naturally promotes emotional regulation. The rhythmic, focused nature of art-making activates the parasympathetic nervous system, counteracting the hyperarousal common in trauma survivors. Artistic media provide a safe container for intense emotions, allowing their expression and transformation without overwhelming the individual.
Through the mastery of artistic techniques and materials, trauma survivors build resilience and self-efficacy, embarking on a journey of trauma healing and resilience. The experience of creating something meaningful from difficult experiences reinforces a sense of agency that trauma often diminishes. This restoration of personal power extends beyond the art studio into daily life.
Evidence-Based Art Therapy Techniques for Trauma
Sensory-based approaches in art therapy help trauma survivors reconnect with their bodies and develop present-moment awareness. Working with tactile materials like clay or textiles grounds clients in physical sensation, countering dissociation and promoting embodied presence.
Narrative techniques enable survivors to tell their stories through visual means, creating coherence from fragmented traumatic memories. Timeline projects, visual journaling, and sequential art help reorganize traumatic material into comprehensible narratives with beginnings, middles, and ends.
Bilateral stimulation – engaging both hemispheres of the brain—occurs naturally in many art therapy processes. Activities that cross the body’s midline or use both hands simultaneously promote neural integration, similar to techniques used in EMDR therapy (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing).
Mindfulness-based art interventions combine present-moment awareness with creative expression, complementing practices like yoga and mindfulness for trauma healing. Mindful drawing, sensory-focused collage, and attentive engagement with art materials help trauma survivors develop greater tolerance for difficult emotions while staying anchored in the present.
Benefits of Art Therapy for Trauma Survivors
Art therapy provides trauma survivors with means for emotional expression that transcend verbal limitations. Through color, shape, texture, and form, survivors can communicate feelings that defy words, including complex emotional states, bodily sensations, and implicit memories associated with their trauma.
Clinical studies demonstrate measurable reductions in PTSD symptoms, anxiety levels, and stress indicators among trauma survivors who engage in regular art therapy, as noted by Psychology Today. These improvements include decreased intrusive memories, reduced hyperarousal, better sleep quality, and enhanced distress tolerance.

The creative process builds critical self-awareness by externalizing internal states, a concept explored in this article from Greater Good Magazine. As survivors review and reflect on their artwork, they gain perspective on their emotions, thought patterns, and trauma responses. This insight forms the foundation for developing healthier coping strategies and more adaptive behaviors.
Art therapy creates a protected environment for healing exploration. The physical space of the art therapy room, combined with the metaphorical space provided by creative expression, establishes safety for processing traumatic material without retraumatization.
Art Therapy Techniques for Trauma Healing
Visual Arts
Visual arts form the core of most art therapy practices. Drawing with pencils, markers, or pastels offers immediate expression with minimal barriers to entry. Painting introduces color psychology and fluid movement, allowing emotional release through gesture and hue. Collage provides structure for those intimidated by “blank canvas” pressure, enabling expression through selection and arrangement of existing images. Sculpting with clay engages tactile awareness and three-dimensional thinking, helping survivors literally reshape their experiences.
Expressive Writing
Writing complements visual expression in trauma recovery. Therapeutic journaling creates space for processing emotions and observations alongside artwork. Poetry distills complex emotional experiences into metaphorical language. Storytelling, whether written or illustrated, helps reorganize traumatic memories into coherent narratives with beginnings, middles, and endings that provide resolution.
Music & Dance Therapy
Sound healing utilizes rhythm, melody, and harmony to address trauma’s impact on the nervous system. Movement-based therapy reconnects trauma survivors with their bodies through dance, authentic movement, or simple gestural expression. Both approaches address the embodied aspects of trauma that remain stored in physical tension patterns and somatic memory.
Digital Art & Photography
Technology offers contemporary avenues for creative expression. Digital drawing and design programs provide precision and control that benefit some trauma survivors. Photography creates opportunities for mindful observation and perspective-taking. Video projects enable dynamic storytelling and narrative development.
Group vs. Individual Art Therapy
Individual art therapy provides personalized attention and maximum privacy for processing sensitive traumatic material. Group therapy offers additional benefits: witnessing others’ healing journeys reduces isolation, group feedback provides multiple perspectives, and the shared creative space builds community support, as exemplified in specialized trauma support for women. The optimal format depends on individual comfort level, trauma history, and treatment goals.
How To Get Started With Art Therapy For Trauma Survivors
Initial art therapy sessions typically include assessment of your history, needs, and comfort with creative materials. Your art therapist will establish safety protocols and explain confidentiality before introducing appropriate creative interventions. Remember that art therapy emphasizes process over product—artistic skill is never required for therapeutic benefit.
Consider art therapy if traditional talk therapy hasn’t fully addressed your trauma symptoms, if you struggle to verbalize your experiences, or if you’re drawn to creative expression. Art therapy also benefits those experiencing physical manifestations of trauma like chronic pain or tension.
The format choice depends on personal preference and specific needs. Individual therapy offers privacy and personalized attention for processing sensitive traumatic material. Group therapy provides community support, reduces isolation, and offers diverse perspectives on your creative work. Many practitioners recommend starting with individual sessions before transitioning to group work as comfort increases.
Finding art therapist for trauma survivors in Denver
Qualified art therapists hold master’s degrees in art therapy or related fields with specialized trauma training. Look for credentials like ATR (Art Therapist Registered) or ATR-BC (Board Certified), indicating recognized professional standards. Denver offers several pathways to find art therapist for trauma survivors in Denver through resources like the American Art Therapy Association’s therapist directory, Psychology Today’s provider listings, or referrals from mental health clinics.
When researching therapists for Trauma Healing Programs, evaluate their specific experience with your type of trauma, theoretical approach, and cultural competence. Most therapists offer initial consultations to assess fit before beginning treatment.

The debate between online and in-person art therapy continues, with benefits to both formats. In-person sessions provide direct material engagement and immediate therapist presence. Online therapy offers accessibility, convenience, and comfort of your own environment. For trauma-focused work, many therapists recommend in-person sessions when possible, especially during initial phases of treatment.
Cost & Accessibility of Art Therapy
The cost of art therapy for trauma survivors in Denver varies based on therapist credentials, session duration, and practice setting. Specialized trauma training typically commands higher rates. Sessions in private practice settings generally cost more than those in community mental health centers. For more info about courses like Individual sessions, Group therapy or Community-based programs, please Call Us by phone number (303) 268-4655(Available 24/7), we are always happy to answer your questions.
Financial options exist to make art therapy more accessible. Many therapists offer sliding scale fees based on income. Nonprofit organizations provide reduced-cost services through grants and donations. Insurance coverage for art therapy has improved, though coverage varies by plan. Some plans cover art therapy under “psychotherapy” when provided by licensed mental health professionals.
FAQs about Art Therapy for Trauma Survivors
Do I need artistic skills to benefit from art therapy?
No. Art therapy focuses on the process of creation rather than the final product. Technical skill has no correlation with therapeutic benefit. Your art therapist will help you find comfortable expression methods regardless of experience level.
How long does it take to see results from art therapy?
Results timeline varies based on trauma severity, duration, and individual factors. Some experience immediate relief through emotional expression, while deeper healing typically requires consistent engagement over months. Most trauma survivors notice gradual improvements in symptoms, emotional regulation, and self-awareness with regular sessions.
Can children and adolescents use art therapy for trauma healing?
Yes. Art therapy works particularly well for young people who may lack verbal skills to process trauma. For those seeking additional evidence-based options, trauma-focused CBT for adolescents can also provide effective support. Developmentally appropriate creative interventions help children express and integrate traumatic experiences without requiring verbal articulation. Many art therapists specialize in working with traumatized children and adolescents.
Is art therapy covered by insurance?
Coverage varies by plan. Many insurance companies cover art therapy when provided by licensed mental health professionals (LPC, LCSW, psychologists) who integrate art methods into treatment. Some plans specifically cover credentialed art therapists. Always verify coverage directly with your insurance provider.
What materials are commonly used in art therapy sessions?
Standard art therapy studios provide drawing materials (pencils, markers, pastels), painting supplies (watercolors, acrylics), collage materials (magazines, scissors, glue), and three-dimensional media (clay, sculpture materials). Therapists select materials based on therapeutic goals, considering factors like control needs, emotional regulation capacity, and symbolic properties of different media.
Conclusion
Art therapy offers trauma survivors a unique pathway to healing that engages both creative expression and psychological processing. Through various art modalities, survivors can access traumatic memories safely, regulate overwhelming emotions, and rebuild a sense of meaning and identity beyond their trauma. The benefits of art therapy for trauma survivors extend beyond symptom reduction to include improved self-understanding, enhanced emotional regulation, and renewed capacity for joy and connection.
If you’re considering art therapy as part of your recovery journey in Denver, Revive Health Recovery offers comprehensive trauma-informed art therapy services. Our experienced therapists understand how to utilize creative approaches within a trauma-informed framework. Reviews of art therapy for trauma survivors at our center consistently highlight the transformative potential of this approach when conducted in a safe, supportive environment.
For more information about our art therapy programs or to schedule an initial consultation, contact Revive Health Recovery today. Our team can answer questions about how art therapy help trauma survivors and guide you toward the most appropriate services for your specific needs.